Electronic Resources in Libraries
Definition
According to Library and knowledge Technology Glossary” Term wont to describe all of the knowledge products that a library provides through a computer network”Need of e-Resources
Electronic Resources enable the librarian to supply better service to the user community. The few considerable points are mentioned below,
To get access to an information source by the quite one user.
E-Resources are often searched quickly.
These are often found easily by the user.
These resources are often stored in huge amounts.
Amount of your time spent on the E-Resources use.
Analyses the aim of using E-Resources by the respondent
Know differing types of E-Resources commonly employed by respondents
To collect, store, organize information in digital form.
To promote efficient delivery of data economically to all or any of the users.
To encourage co-operative efforts to save lots of and share the investments in research resources, computing and communication network.Types of Electronic Resources

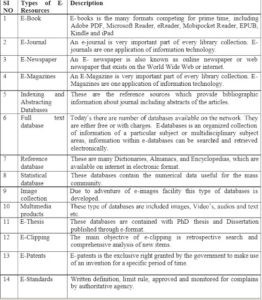
types of e-resources Utilities of e-Resources Electronic Resources in Libraries
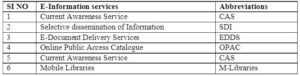
Nowadays the reading materials and knowledge sources are changing from print to electronic. a number of such E-Information services are detailed and briefly discussed here.

Utility of e-Resources Selections of Electronic Resources
The selection of E-Resources should be done consistent with the necessity and demand of users. As a librarian one should consider the subsequent steps at the time of selection.
To know the necessity of users.
To know the content and scope of e-resources.
To examine the quality of the e-resources and search facility among them.
To maintain cost-effectiveness.
To check either subscription base or web-based at the time of buying.
To check the license copy.
To evaluate educational support and training.
To check compatibility and technical support.Characteristics of Electronic Resources
Access to each document by anyone; from anywhere
Retrieval of e-resource is quicker than print resources
The users are often guided to the document by providing a link
Easy to look at the text
The collection available in electronic format are often any media.
Ownership not that important
In the electronic environment, the interaction between user and librarian is frequent
No defined user group
The software can help the users in retrieving the specified information, hardly intermediate can help usersAdvantages of Electronic Journals:
The Contents of pages and/or the complete text of journals are often easily acknowledged and articles associated with any certain subject are often easily searched.
Journal articles are on your desktop; you do not need to be within the Library.
It is often very easy to email articles to yourself or downloads them for printing.
The article that you simply want to read will always be available, even when the Library is closed.
Hypertext links allow you to maneuver to different section s within individual journals or articles and may link you to related resources on the web.
Journals can include more image and audio-visual material
Journals are often interactive you’ll e-mail the author or editor together with your comments.Disadvantages of Electronic Journals:
Difficulty in reading.
Highly expensive resource.
Needed High Infrastructure.
Needed User Training to access.
Excessive Printing of documents.Open Educational Resources: Open Educational Resources (OER) are those teaching and learning materials that are available to anyone freed from cost and under an open license to permit others to retain, reuse, remix and redistribute them with few or no restrictions.
Open Educational Resources include textbooks, online tutorials, lecture notes, lesson plans, slides handouts given to students, videos, podcasts, diagrams, entire courses, and the other material designed to be used in teaching and learning.
Open Courseware
Open Textbooks
Open LearningStakeholders: Stake holders of OER include teachers in the least levels of education, administrators, policymakers, library professionals, civil society organizations, and individuals with an interest in promoting access to educational resources.
Bearer in Electronic Resources
Lack of your time, lack of awareness, and low Internet connectivity
Lack of data on the standard of OER
Scarcity of OER in video and audio formats————————————————————————————————————————–
Indian Initiatives
e-Pathshala
ePathshala NCERT books available free in digital version
15 lakh students have to download the e-pathshala apphttp://epathshala.gov.in
————————————————————————————————————————–National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER)

Nroer A platform to gather or provide digital and digitizable resources of a faculty education and teacher education across India.
http://nroer.gov.in
Launched on 13 August 2013
NROER may be a collaborative platform provide by which brings together everyone curious about school and teacher education across India.
NROER may be a comprehensive digital repository of resources that will be employed by teachers within the teaching-learning process.
The idea is to form a sort of resources available to teachers.—————————————————————————————————————-
E-PG Pathshala: A Gateway to all or any postgraduate course

e-PG Pathshala ——————————————————————————–
National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL)
NPTEL NPTEL Launched in 2003.
NPTEL was initiated by seven Indian Institutes of Technology (Bombay, Delhi, Kanpur, Kharagpur, Madras, Guwahati, and Roorkee along side the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore in 2003.
Five core disciplines were identified, namely, engineering, computing and engineering, EE, electronic & communication engineering, and mechanic engineering in phase I clinical trial.
235 courses in web/video format were developed.
In phase II clinical trial (2009-14), a further 600 web and video course created altogether major branches of engineering, physical sciences UG and PG levels, and management course at the PG level.
Improvements like indexing of all video and web course & keyword search were introduced in the phase II clinical trial.
NPTEL began offering open online courses/ MOOCs in March 2014 alongside certifications for those that completed the Courses successfully.
The advanced courses are being recommended to AICTE to be approved as Faculty Development Programs (FDP).—————————————————————————————————————-
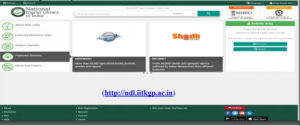
National Digital Library of India

National Digital Library of India Launched in May 2016 (Pilot) & Dedicated to the state on June 19, 2018.
It is a National Mission Project by MHRD &IIT Kharagpur to empower citizens Digital literacy.
————————————————————————————————————–
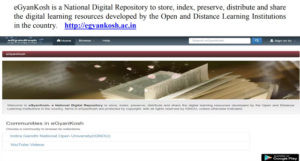
egyankosh ————————————————————————————————————————–
Impact of e-Resources on Library and Knowledge Services
The Internet e-resources are transforming the library system and also the way during which we view we view information sources. it’s made the simple and speedy purchase of data sources like books, journals, and electronic publications. Many publishers catalog tools like ‘Books in prints’ also as forms for ordering documents are available on the web.
The librarians need quick access to books, journals, and electronic publications. Internet access is that the simple and efficient method for access and updating the documentation and interface of the catalog of all libraries. the request for Inter Library Loan (ILL) is often sent via e-mail and therefore the photocopies could also be sent by post fax, via e-mail after scanning the documents.
The development of data technology and therefore the dissemination of Web environments have a dramatic effect on the user behaviors in information usage. The workflows form acquisitions to user services and therefore the life cycle of electronic resources is sort of different from that of print resources since it’s characterized by access without holding the physical objects.
Most of the Library resources within the recent past are being made available in electronic formats like e-journals, e-books, databases, etc. Libraries are moving from print to e-resources either subscribing individually or through consortia due to its advantages over electronic resources have greatly increased in recent years, libraries have struggled to regulate this information in paper files, integrated library systems, separate databases store on local computers or network
Utilities of e-Resources
E-publishing could also be less expensive than paper.
E-Resources are created in any file format like text, audio, video, and pictures.
E-Resources are available for twenty-four hours of each day and save library space
The E-Resources search is straightforward due to the user-friendly interface.
They provide users faster, more convenient, and anytime access from home, campus, or library.
E-resources are often accessed by the support of an advanced search and retrieval systems.
Libraries are focused on providing access to primary information.Issues of e-Resources
Licensing: E-resources need the license from the published to the library for creating use of it.
IPR: E-resources are often easily copied and forwarded to another person so librarian should be alert about IPR(Intellectual Property Rights)Standards of metadata: There are standards for metadata description like MARC21 but the available e-resources within the market aren’t standardizing by MARC21
Low Budget: Libraries are non-profit organizations in order that they cannot purchase and afford costly electronic resources.Skill manpower: to handle the electronic collection the right skills are required among the staff but libraries are lacking skill manpower
Lack of infrastructure: Electronic collections supported by Information and communication technology components
References:
Abbas Khan, A. A., Minhaj F. & Ayesha, S. (2007), E-resources: E-books and E-Journals In E-Libraries: Problems and perspectives, Ed. by Ramish, Sankara Reddy and Hemant Kumar. Allied, New Delhi.
Barman Badan (2012), Library and knowledge Science: UGC NET guide, DVS Publishers, Guwahati, 125-126.
Kenchakkanavar, Anand Y. (2104), sorts of E-Resources and its utilities in the library, International Journal of Data Sources and Services, Vol I, No 2. PP 97-104.Koha Software Customization Click Here