Definitions
“By far the best danger of AI ,” AI theorist Eliezer Yudkowsky has observed, “is that folks conclude too early that they know it .”20 intrinsically , it’s important to first properly delineate what AI is – or are often . To do so, we must first grasp what general intelligence refers to.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a neighborhood of computing that aims at reducing the gap between man and machine. Or in other words, it aims at creating machines that behaves or reacts like humans.
Hence machines are empowered with different human abilities both mental and physical – which cause various directions of research:
The Pioneers of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence and knowledge Age Contribution of Boole

Developer of Boolean logic
The foundation of data Age

Father of Theoretical computing and AI

The subfield of computing concerned with understanding the character of intelligence and constructing computer systems capable of intelligence action. AI (Winston, 1999)
Intelligence
Intelligence may be a cornerstone of the human condition .It is a mental activity that we, as citizenry , are uniquely qualified to exercise. Different elements of and processes within your brain, making use of other parts of your biology (e.g. your eyes), work together to form possible the act of reading and comprehension
‘Intelligence’, conducted by Legg & Hutter, argues that it’s hard to choose one ‘correct’ term, however they are doing note that a lot of of the foremost concise and precise definitions share variety of features:
(1) intelligence may be a property of some agent that interacts with an environment;
(2) intelligence is usually indicative of that agent’s ability to succeed at a specific task or stated goal;
(3) there’s a stress on learning, adaptation, and adaptability within a good range of environments and scenarios.
Artificial Narrow-, General-, and Superintelligence
• Artificial Narrow Intelligence(ANI or “narrow AI”)43: machine intelligence that equals or exceeds human intelligence for specific tasks. Existing samples of such systems would be IBM’s Deep Blue (Chess) & Watson (‘Jeopardy!’), Google’s AlphaGo (go), High-Frequency Trading Algorithms, or indeed any specialized automatic systems performing beyond human reach (e.g. Google Translate; spam filters; the guidance systems of point-defense anti-missile cannons etc.).
• Artificial General Intelligence (AGI or “strong AI”): machine intelligence meeting the complete range of human performance across any task; and:
• Artificial Superintelligence(ASI): machine intelligence that exceeds human intelligence across any task.
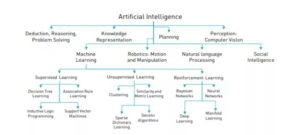
AN OVERVIEW OF NOTABLE APPROACHES AND DISCIPLINES IN AI AND MACHINE LEARNING
By analogy to those components constituting human cognition, what, then, is that the library of intelligent sensory-, information-processing-, pattern-matching- and categorization functions underlying artificial intelligence? As represented in Figure , at its highest level, AI problems cluster around several classes. the primary of those concerns the matter of correctly parsing inputs, which deals with problems with perception; computer vision; tongue processing; and taking appropriate cues from social intelligence; the second of those involves correctly planning & executing outputs (‘behavior’), which involves appropriate processes for knowledge representation, prioritization, planning and, in embodied AI systems, robotics (system motion; collision avoidance; manipulators).
In other words, the idea and development of computer systems ready to perform tasks that normally requires human intelligence like beholding , Speech Recognition, Decision-Making and Translation Between Languages.
Artificial Intelligence focuses on:
Search and Optimization
Fuzzy System
tongue Processing and Knowledge Representation
Computer Vision
Machine Learning and Probabilistic Reasoning, Planning and Decision-Making
Neural Works
Components of Artificial Intelligence
Logic and Rules Based
Computer makes decisions supported a choice tree, logic rules or a predefined process with a calculated result.
Pattern Based (Machine Learning)
Computer learn overtime by using data and algorithms to detect patterns.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning may be a subset of Machine Learning that permits the pc to form decisions on its own.
Neural Networks
A neural networks allows an AI to form its own conclusions, where an easy pattern- only based AI must rely solely on data. A neural network allows deep learning to functions.
Natural Language Processing
Allows a computer to know the most linguistic concepts within an issue or solution. Its goal is to style and build computer that analyze, understand and generate language that human use naturally
Natural Language processing — Knowledge Representation —Automated Reasoning — Machine Learning
Why AI is required in Libraries.
Quick access to information
Helps to increase library services
These services are going to be popular in future
Helps users to familiarize with the knowledge available in library
These services are essential for a library
Helps to reaching bent more users
Helps users to up-to-date with modern technologies
Helps users to conversant in library activities
Helps library staff to scale back work load
Helps to enhance physical usage of library
Artificial Intelligence and its Applications in Libraries
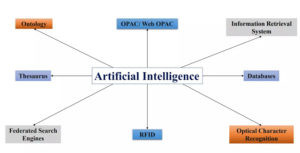
An Expert System helps the librarian in realizing the necessity for an improvement within the library operations and services. A well programmed Expert System improve the standard of the operations and services.
Ask Librarian
The Expert System works as a substitute for a reference librarian
Application of Expert Systems Classification .
1 Coal SORT(Semantic Network)
A Knowledge-Based Interface
Designed to serve either as an enquiry or an Indexing Tool
2 BIOSIS (an Indexer Aid)
To assign documents to categories automatically
The indexing languages are structured and practical representation of data .
Uses the knowledge within the titles of biological documents.
Cataloguing and DCMI
Focused on descriptive cataloguing because it’s considered rule-based (AACR2)
A Human-Machine Interface An Expert System with full cataloguing capability
AI Based Reference Management Tools
REF-SEARCH POINTER
are often wont to teach student’s reference skills.
As a computerized aid for practicing reference librarians and knowledge specialists.
PLEXUS
A referral tool utilized in Public Libraries
POINTER
Directs the users to the reference sources.
Best software for references
Zotero
Mendeley
Endnote
Citavi
Refworks
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Can combat stressful and sophisticated work that humans may struggle/cannot do;
Can complete task faster than a person’s can most likely;
to get unexplored things. e.g., outer space;
Less errors and defects;
Function is infinite.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Lack of “human touch”;
Has the power to exchange human jobs;
Can malfunction and do the other of what they’re programmed to do;
are often misused resulting in mass scale destruction;
May corrupt younger generation.
Challenges of Artificial Intelligence
Precision
The idea of garbage data in garbage data out. If you flood an AI with bad data and do not set the right syntax or thresholds you’ll get incoherent results.
Context
Artificial Intelligence can struggle with understanding context. for instance , asking Siri”call me an ambulance” may yield “OK, form now on, i will be able to call you Ambulance”
Training
Similar to having good data, an AI might got to learn the right response for the right situation or identify dangers or inappropriate interactions.
References
Stephan De Spiegeleire, Matthijs Maas and Tim Sweijs.(2017).Artificial Intelligence and therefore the way forward for defense. Hague Centre for Strategic Studies.https://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep12564.7
Shibin, S.B, (2020).Artificial Realities in Library Services: A Study regarding Perspectives of Library Professional.PEARL – A Journal of Library and knowledge Science Vol. 14, No. 1, January-March 2020: 41-49
KP, Singh.(2019). Application of AI and Machine Learning in Library Operations and Services. ETTLIS, Swayam.
